Potential role of ACE2-related microRNAs in COVID-19-associated nephropathy
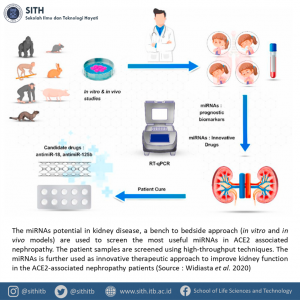
The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is responsible for coronavirus disease (COVID-19), potentially have severe kidney adverse effects. This organ expressed angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2), the transmembrane protein which facilitate the entering of the virus into the cell. In this review article, Dr. Husna Nugrahapraja and his colleagues summarized the novel miRNA-based therapy and its potential applications in COVID-19-associated nephropathy, highlighting several miRNAs which played a crucial role in ACE2 expression.
Article Citation:
Widiasta,A.,Sribudiani,Y.,Nugrahapraja,H.,Hilmanto,D.,Sekarwana,N.,Rachmadi,D.2020. Potential role of ACE2-related microRNAs in COVID-19-associated nephropathy. Non-coding RNA Research, 5: 153-166.
Full paper is published in Non-coding RNA Research : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncrna.2020.09.001
Image (first page):
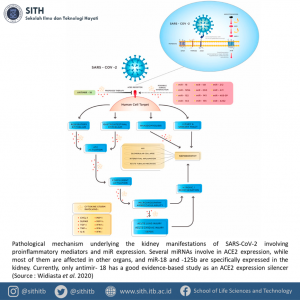
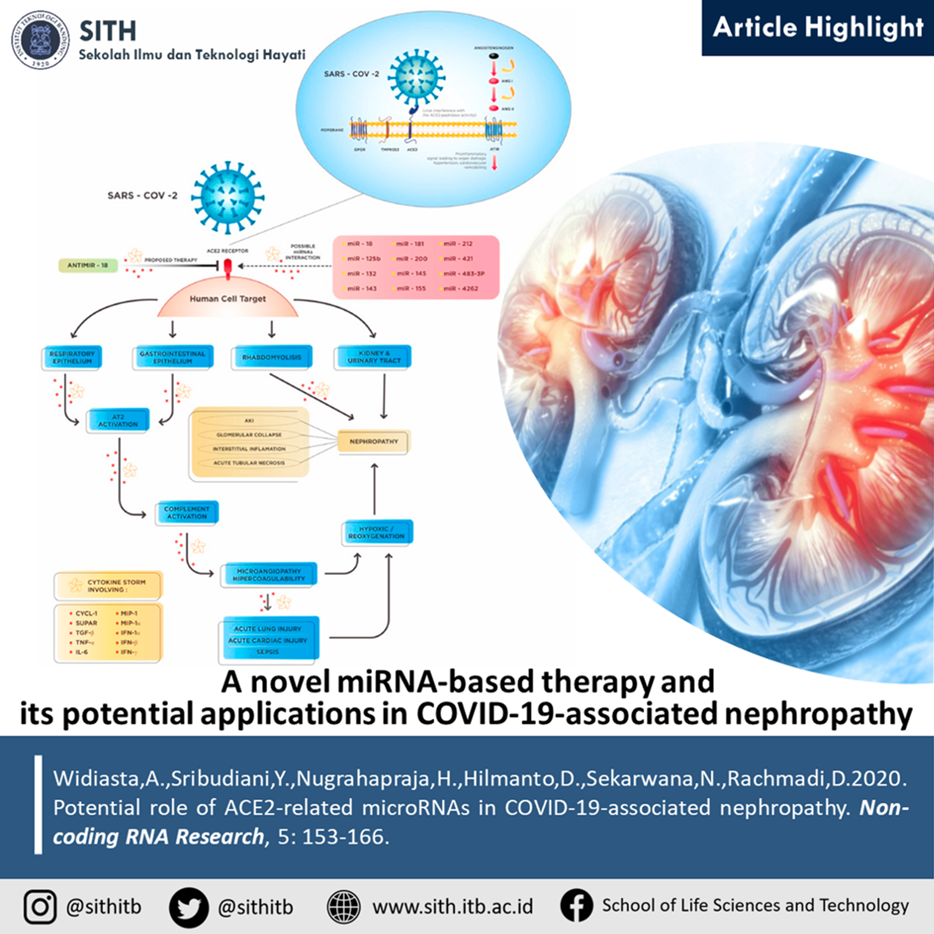
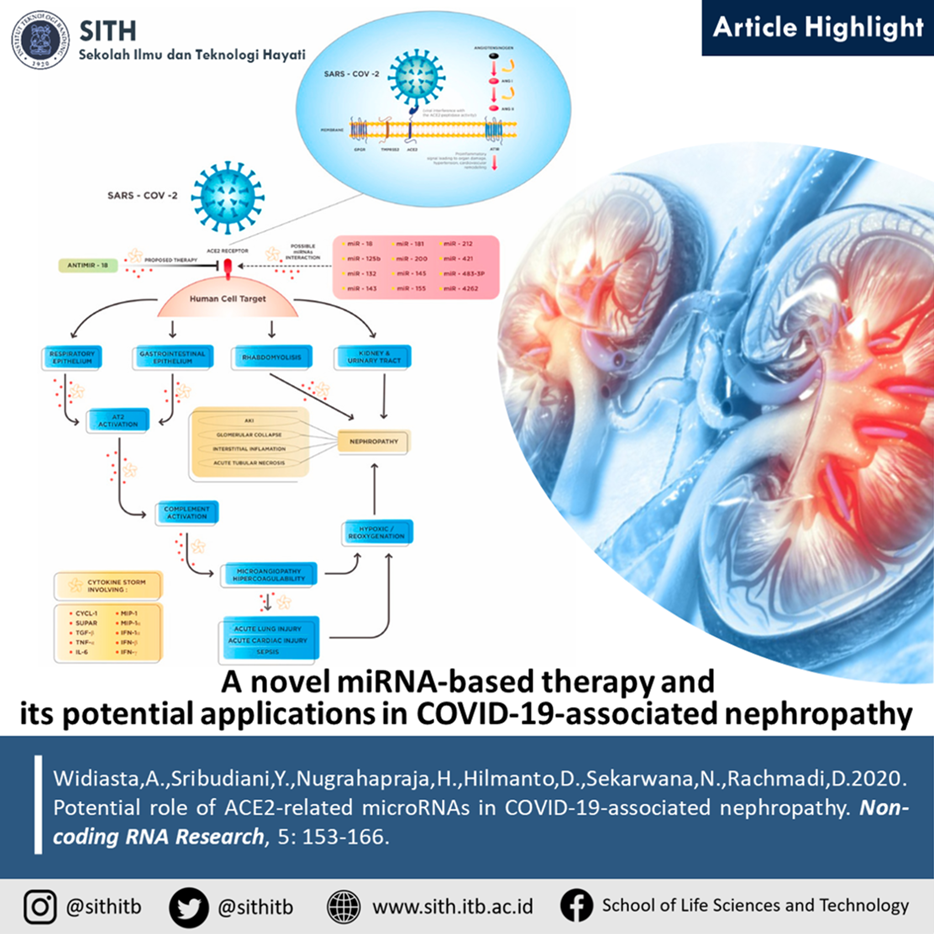
Pathological mechanism underlying the kidney manifestations of SARS-CoV-2 (Source: Widiasta et al. 2020)
Kidney illustration (source: healio.com)
Profile of Dr. Husna Nugrahapraja: https://sith.itb.ac.id/en/husna-nugrahapraja-ph-d/