Nutritional profiling of microfungi and its effects on the growth performance, bacterial communities, and survival with Vibrio harveyi on white shrimp post-larvae (Litopenaeus vannamei)
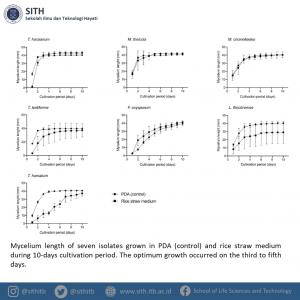
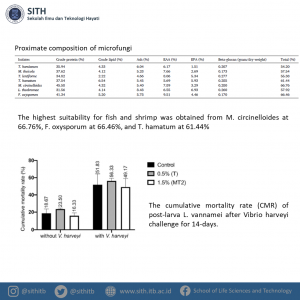
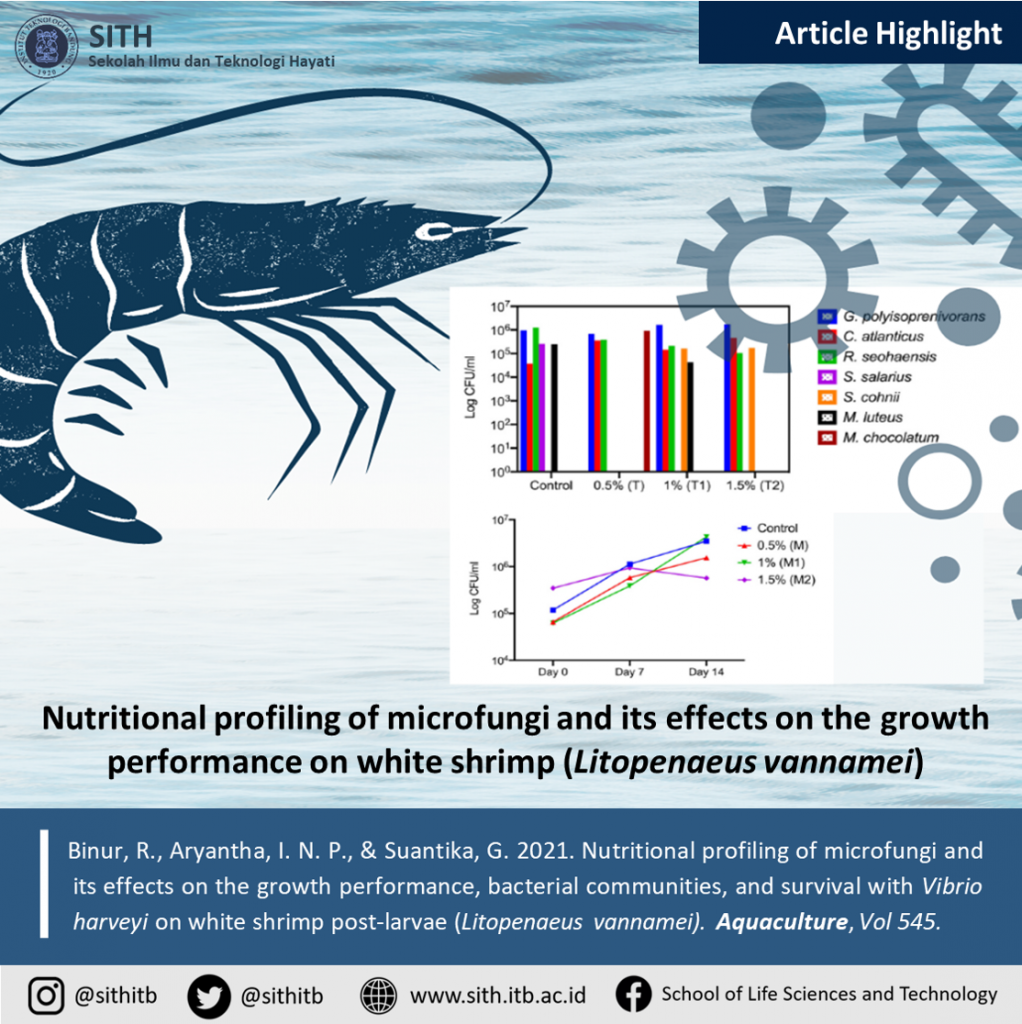 Aquaculture industries would benefit from the cultured organisms conferred with feed supplements for optimal growth and disease resistance. In this study, Prof. Dr. I Nyoman Pugeg Aryantha and colleagues evaluated seven microfungi isolated from rivers or streams in Indonesia for a nutritional profile including protein, lipid, amino acids, fatty acids, and beta-glucan. All isolates had relatively high nutritional content, where the proteins ranging from 31.56–45.58%, lipids 2.22–6.54%, amino acids 11.023–18.881 g/100 g, fatty acids 1.094–5.253%, and beta-glucan 0.170–0.280 g/dry weight. The results indicated that T. harzianum fed with 0.5% and 1.5% could improve white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) post-larvae survival and growth performance. It was found that two dominant bacteria were Gordonia polyisoprenivorans and Croceibacter atlanticus.
Aquaculture industries would benefit from the cultured organisms conferred with feed supplements for optimal growth and disease resistance. In this study, Prof. Dr. I Nyoman Pugeg Aryantha and colleagues evaluated seven microfungi isolated from rivers or streams in Indonesia for a nutritional profile including protein, lipid, amino acids, fatty acids, and beta-glucan. All isolates had relatively high nutritional content, where the proteins ranging from 31.56–45.58%, lipids 2.22–6.54%, amino acids 11.023–18.881 g/100 g, fatty acids 1.094–5.253%, and beta-glucan 0.170–0.280 g/dry weight. The results indicated that T. harzianum fed with 0.5% and 1.5% could improve white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) post-larvae survival and growth performance. It was found that two dominant bacteria were Gordonia polyisoprenivorans and Croceibacter atlanticus.
Article Citation: Binur, R., Aryantha, I. N. P., & Suantika, G. 2021. Nutritional profiling of microfungi and its effects on the growth performance, bacterial communities, and survival with Vibrio harveyi on white shrimp post-larvae (Litopenaeus vannamei). Aquaculture, Vol 545.
Full paper is published in Aquaculture : https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2021.737260
Image (first page):
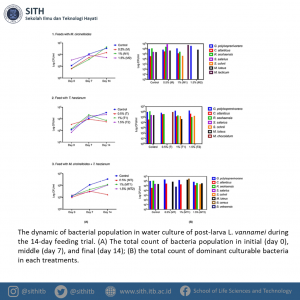
The dynamic of bacterial population in water culture (Source: Binur et al., 2021)
Graphics by canva : https://www.canva.com/
Profile of Prof. Dr. I Nyoman Pugeg Aryantha :
https://sith.itb.ac.id/inyomanpugeg/