Nocturnal Blue Light Exposure Increase Alpha and Beta Brain Waves as Cognition Function for Two Consecutive Night Driving in a Car Simulator
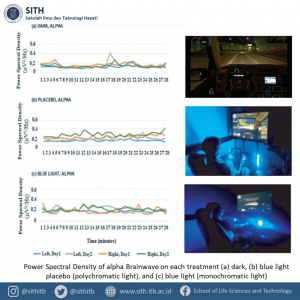
 Driving is a complex activity that engage complex motor, sensor, and cognitive function which can be analyzed through brain wave using electroencephalograph (EEG). Decrease of cognitive function while driving in long period at night linked with drowsiness and exposure of blue light to driver in night-driving could improve cognitive function. In this article, Dr. Lulu L. Fitri and colleagues studies nocturnal blue light exposure in longer duration and its effect in brain cognitive function, suggesting that repeated, continuous exposure of blue light may increase alpha and beta wave power spectral density, in which monochromatic blue light causes better cognitive state than polychromatic blue light.
Driving is a complex activity that engage complex motor, sensor, and cognitive function which can be analyzed through brain wave using electroencephalograph (EEG). Decrease of cognitive function while driving in long period at night linked with drowsiness and exposure of blue light to driver in night-driving could improve cognitive function. In this article, Dr. Lulu L. Fitri and colleagues studies nocturnal blue light exposure in longer duration and its effect in brain cognitive function, suggesting that repeated, continuous exposure of blue light may increase alpha and beta wave power spectral density, in which monochromatic blue light causes better cognitive state than polychromatic blue light.
Article Citation:
Fitri, LL., Prestiasani, K., Suprijanto. 2020. Nocturnal Blue Light Exposure Increase Alpha and Beta Brain Waves as Cognition Function for Two Consecutive Night Driving in a Car Simulator. Sains Malaysiana. 49(9): 2091-2099.
Full paper is published in Sains Malaysiana: http://journalarticle.ukm.my/15905/
Image (first page):
Car simulator installation, Power Spectral Density of alpha Brainwave, and Blue Light LED (Monochromatic) in car simulation (Fitri et al. 2020)
Profile of Dr. Lulu L. Fitri:
https://sith.itb.ac.id/en/lululf/