[:id]
Standar Pelayanan
Tahapan Identifikasi dan Determinasi Tumbuhan/Hewan
- Membuat surat permohonan kepada Wakil Dekan Bidang Sumberdaya SITH ITB di Gedung Labtek XI Lantai I, Jalan Ganesha No. 10, Bandung 40132 dari instansi pemohon yang disahkan oleh pejabat berwenang.
- Membayar biaya Identifikasi/ Determinasi melalui rekening Bank BNI :
Penampungan SITH-ITB No : 0901062011
Biaya identifikasi dan determinasi :
Rp. 55.000,- (lima puluh ribu rupiah) per sampel untuk tumbuhan,
Rp. 110.000,- (seratus ribu rupiah) per sampel untuk hewan
Khusus untuk mahasiswa S1 dan S2 SITH ITB, biaya identifikasi setengah dari tarif yang berlaku dengan megajukan permohonan identifikasi/determinasi yang ditandatangani (diketahui Pembimbing)
Untuk Perusahaan tarif yang berlaku dua kali lipat dari tarif yang berlaku
Pembayaran hanya dilakukan melalui teller dengan mencantumkan
- Nama penyetor mahasiswa ybs.
- NPWP bagi yang memiliki atau No. KTP/ NIK
- Pada kolom Berita dicantumkan jenis tumbuhan/ hewan yang akan diidentifikasi/ determinasi berikut nama mahasiswa dan NIM/ NPM
3. Fotokopi surat permohonan diserahkan bersama dengan:
a. Bukti Pembayaran dari Bank BNI
b. Spesimen tumbuhan/ hewan yang akan diidentifikasi
Persyaratan kondisi sampel tumbuhan yang akan diidentifikasi :
- Tumbuhan segar maupun tumbuhan yang telah dipreservasi dengan alkohol. Berikut adalah cara preservasi tumbuhan untuk keperluan determinasi: Spesimen dimasukkan dalam kertas koran dan diikat dengan tali rafia. Kertas koran yang telah berisi spesimen lalu dimasukkan dalam plastik sampah bening dan disiram dengan alkohol 70%. Selanjutnya plastik direkatkan dengan lakban.
- Apabila sampel berupa ganggang/alga, maka sampel yang dibawa harus lengkap dengan alat reproduksinya dan dimasukkan dalam wadah tertutup rapat berisi alkohol 70%.
- Apabila sampel berupa lumut, maka sampel yang dibawa harus seluruh bagian yang dilengkapi dengan organ reproduksinya.
- Apabila sampel berupa tumbuhan paku (Pteridofita) maka sampel yang dibawa harus lengkap dengan akar, batang, daun steril (tropofil), dan daun fertil yang mengandung sorus (sporofil) (Gambar 1). Khusus untuk paku berukuran besar, maka bagian yang dibawa adalah potongan tangkai daun dan daun fertil serta daun steril yang utuh (Gambar 2).
- Apabila sampel berupa tumbuhan herba maka sampel yang dibawa harus lengkap dengan akar, batang, daun, bunga dan buah (Gambar 3). Jika buah tidak tersedia maka cukup dengan bagian bunga. Khusus untuk tumbuhan herba berukuran besar, seperti honje, tepus, atau pisang, maka sampel yang dibawa terdiri dari daun, karangan bunga, dan buah (Gambar 4)
- Apabila sampel berupa semak, perdu atau pohon, maka sampel yang dibawa adalah ranting sepanjang 30 cm yang lengkap dengan daun, bunga dan buah (Gambar 5). Sampel yang dibawa diusahakan dalam kondisi lengkap (terdiri dari ranting, daun, bunga maupun buah). Jika buah tidak tersedia maka cukup dengan bagian bunga.
- Apabila sampel berupa bambu, maka sampel yang dibawa adalah potongan buluh, pelepah, daun, dan jika memungkinkan bagian bunga serta buahnya (Gambar 6).
- Apabila sampel berupa rotan, maka sampel yang dibawa adalah potongan batang, potongan tangkai daun, potongan daun, flagel (biasanya terletak di bagian ujung daun), satu karangan bunga, dan buah (Gambar 7).
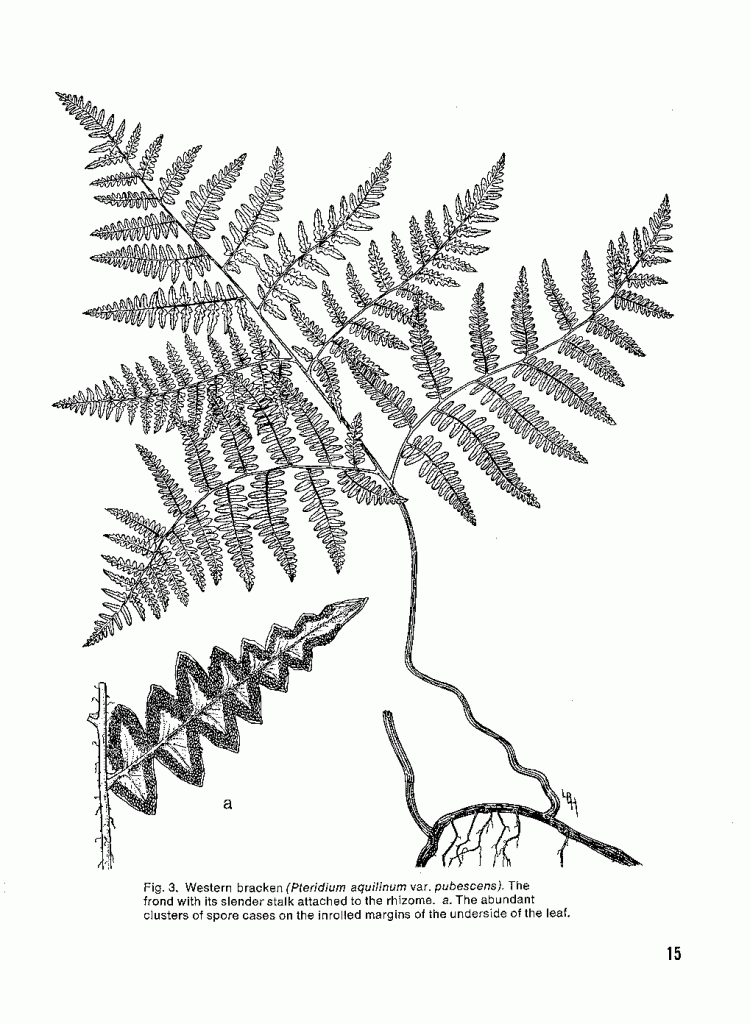
Gambar 1. Sampel tumbuhan paku. Bagian yang dibawa untuk determinasi berupa akar, batang, daun steril, dan daun fertil (Sumber foto: http://v3.boldsystems.org).

Gambar 2. Sampel paku pohon. Bagian yang dibawa untuk determinasi berupa potongan tangkai daun, daun steril yang utuh, dan daun fertil yang utuh. (Sumber foto: http://v3.boldsystems.org).
Gambar 3. Sampel tumbuhan herba berukuran kecil. Sampel yang dibawa untuk determinasi yaitu bagian yang lengkap, mulai dari akar, batang, daun, hingga organ reproduksi (bunga dan buah). (Sumber foto: http://portal.cybertaxonomy.org).
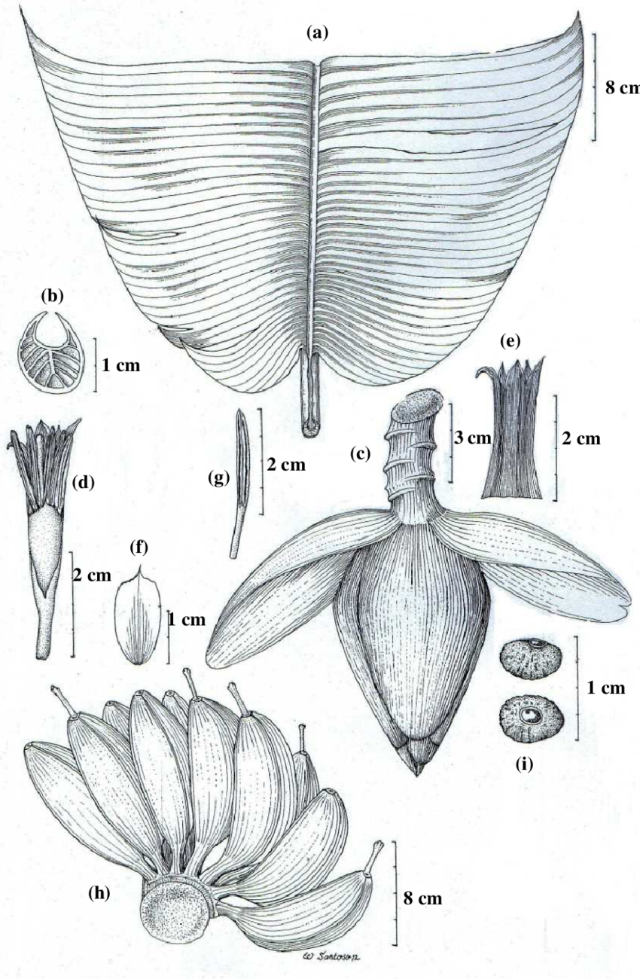
Gambar 4. Sampel tumbuhan herba berukuran besar. Sampel yang dibawa berupa daun, karangan bunga, dan buah (Sumber foto: researchgate.net).
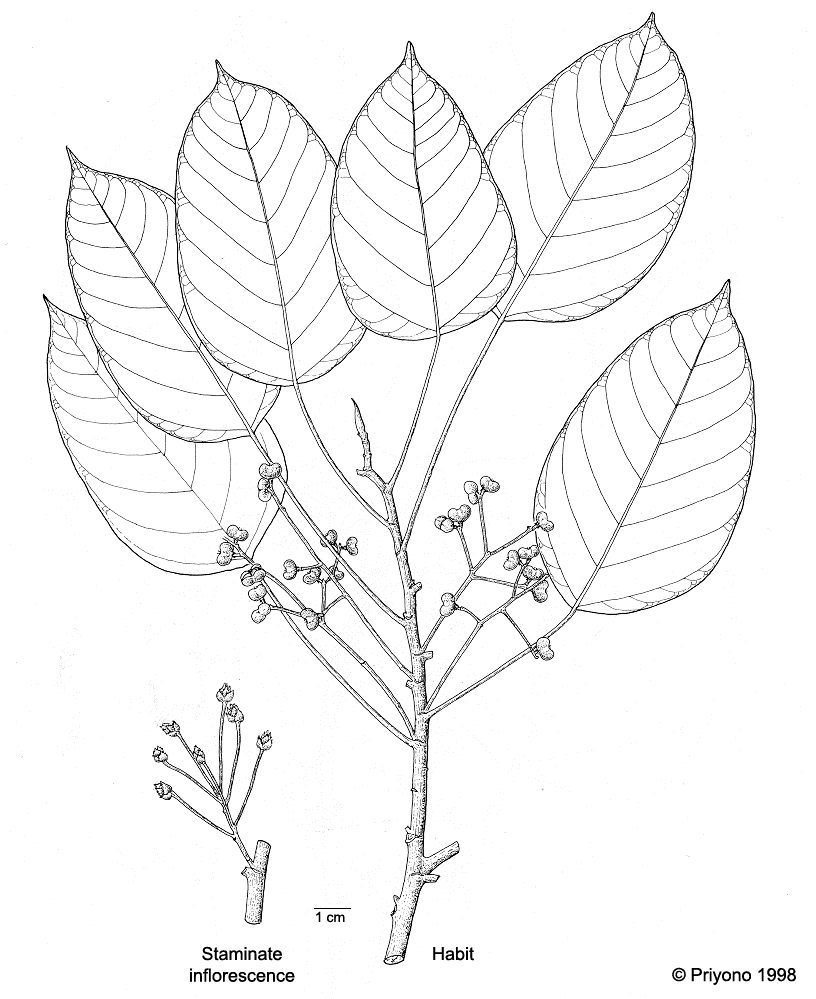
Gambar 5. Sampel tumbuhan berupa semak, perdu atau pohon. Sampel yang dibawa berupa ranting sepanjang 30 cm, lengkap dengan daun, bunga dan buah.
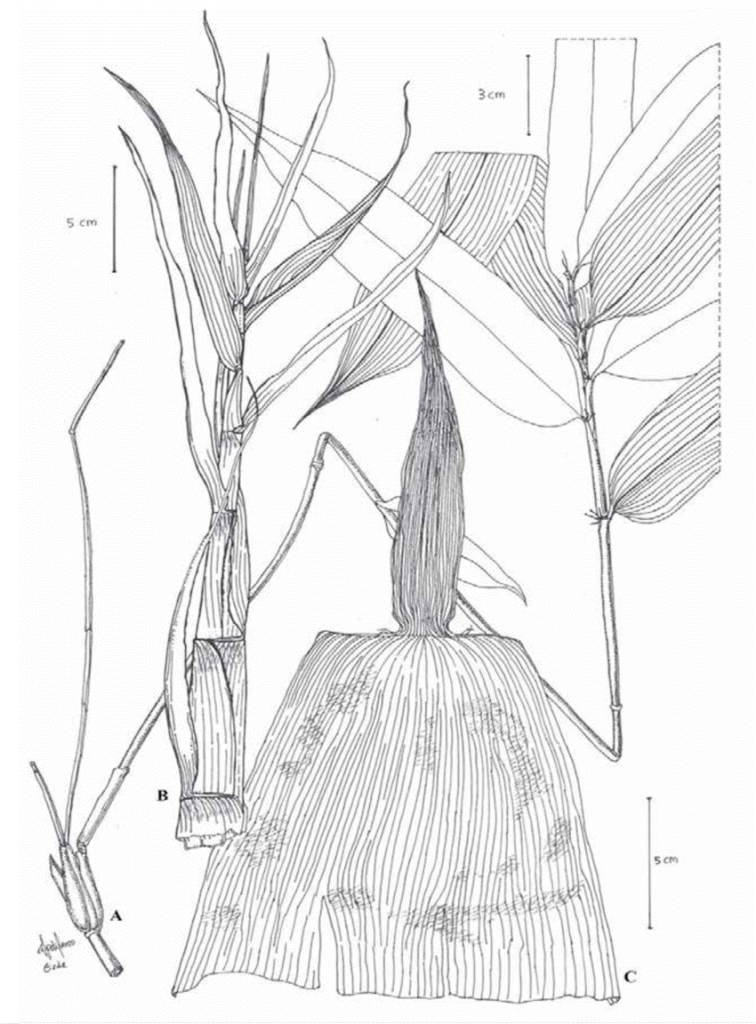
Gambar 6. Sampel bambu. Sampel yang dibawa berupa potongan buluh, pelepah, daun, serta organ reproduksi (bunga dan buah) jika memungkinkan (Sumber foto: researchgate.net).
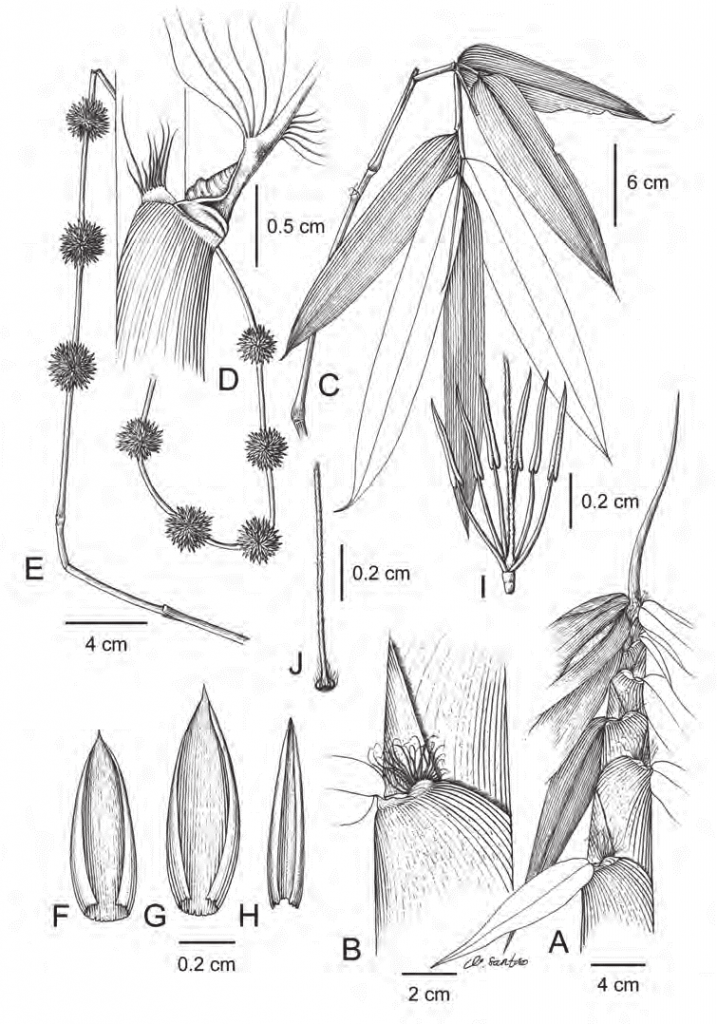
Gambar 6. Sampel bambu. Sampel yang dibawa berupa potongan buluh, pelepah, daun, serta organ reproduksi (bunga dan buah) jika memungkinkan (Sumber foto: researchgate.net).
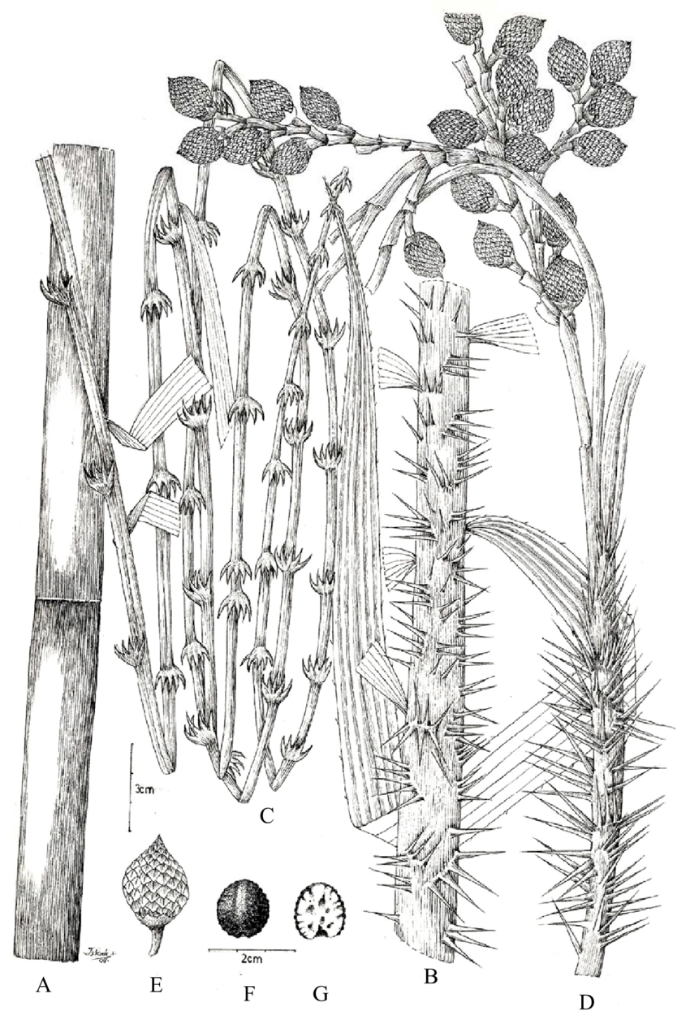
Gambar 7. Sampel rotan. Sampel yang dibawa berupa potongan batang, potongan tangkai daun, potongan daun, flagel, dan organ reproduksi (bunga dan buah) jika memungkinkan (Sumber foto: researchgate.net).
Persyaratan kondisi sampel hewan yang akan diidentifikasi :
Spesimen utuh dengan bagian tubuh yang lengkap, tidak ada yang rusak, atau hilang dibawa dalam keadaan hidup dengan ketentuan sebagai berikut:
- Spesimen sudah dewasa (kecuali larva serangga) dan memiliki ukuran maksimal 1 meter.
- Spesimen dibawa dalam substrat yang sesuai:
- Air laut: untuk hewan yang berasal dari laut seperti ikan laut, teripang, kepiting/ rajungan, udang-udangan, Artemia, ubur-ubur, cumi-cumi, bintang laut, siput laut dan bulu babi.
- Air tawar: untuk hewan yang berasal dari perairan tawar seperti ikan air tawar, belut, kepiting air tawar, siput air tawar, cacing parasit dan serangga air.
- Tanah: untuk spesimen yang hidup di tanah seperti cacing tanah dan serangga tanah.
- Substrat tumbuhan di dalam wadah atau kandang: untuk spesimen yang hidup pada tumbuhan tertentu atau spesimen yang bisa disimpan dalam substrat tumbuhan seperti serangga, amfibi, reptil, ayam dan burung serta mamalia kecil.
Spesimen utuh yang telah terawetkan dengan baik dengan ketentuan sebagai berikut:
- Spesimen telah difiksasi dengan memakai 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin, yaitu komposisi yang terdiri dari pengenceran formalin 40% (100 mL), air (900 mL), dan dicampur 4 gram sodium dihydrogen phosphate, monohydrate (NaH2PO4.H2O) dan 6,5 gram disodium hydrogen phosphate, anhydrous (Na2HPO4) per liter. Bisa dilihat di http://stainsfile.info/StainsFile/prepare/fix/fixatives/formalin-buffered.htm
- Neutral Buffered Formalin harus diinjeksikan pada spesimen yang memiliki cangkang keras seperti kepiting dan rajungan atau daging tebal dan rongga tubuh seperti ikan, amfibi, dan reptil dan didiamkan minimal 3 hari sampai spesimen terfiksasi dengan baik.
- Spesimen dibilas dengan air setelah mengeras sampai kandungan Neutral Buffered Formalin minimal dan baunya tidak terlalu menyengat.
- Spesimen dimasukkan ke dalam wadah dengan penutup rapat (botol kaca, wadah plastik atau vial) dan direndam dalam alkohol 70%.
- Untuk spesimen dengan ukuran besar (>50 cm), pada saat penyerahan bisa dibalut dengan kain kassa yang sudah jenuh dengan alkohol 70% dan dimasukkan ke dalam wadah.
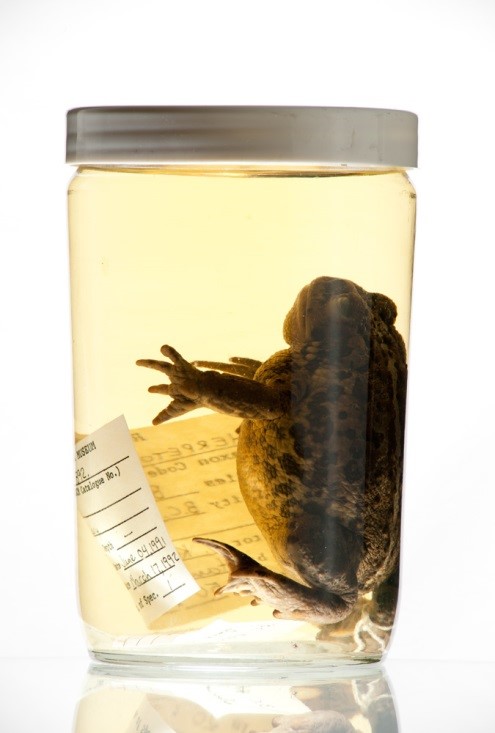

Gambar 8. Contoh spesimen yang telah difiksasi dengan Neutral Buffered Formalin dan direndam dalam alkohol 70% (Sumber: Royal BC Museum).
Spesimen utuh yang diawetkan dalam freezer dan dibawa dengan menggunakan icebox.
Contoh spesimen yang bisa dibawa dengan cara ini misalnya ikan air tawar, ikan laut, udang-udangan, rajungan/ kepiting, cumi-cumi, dan ubur-ubur.

Gambar 9. Contoh spesimen yang diawetkan di dalam icebox (Sumber: http://www.coolersonsale.com).
Spesimen tumbuhan/ hewan tidak disarankan dititipkan:
melainkan dibawa langsung beserta bukti pembayaran, surat permohonan identifikasi atau determinasi asli serta salinannya ke :
Gedung Herbarium Bandungense dan Museum Zoologi, SITH – ITB
Kampus ITB Jatinangor, Labtek V C, samping Mesjid Al-Jabbar.
Contact person untuk Determinasi Tumbuhan
Arifin Surya Dwipa Irsyam S.Si, M.Si (0857 8052 6704)
Contact person untuk Determinasi Hewan:
email : museum-zoologi@sith.itb.ac.id
Pengambilan surat hasil determinasi dapat dilakukan di kantor Tata Usaha SITH ITB, Gedung Labtek XI Lantai I SITH ITB.
[:en]Steps in the Plant/Animal Identification and Determination
- Write a request letter to the Vice Dean of Resources SITH ITB, Labtek XI building, 1st Floor, Jalan Ganesha No. 10, Bandung 40132 from the institution of the applicant, signed by the appropriate officer.
- Pay the Identification/ Determination fee at Bank BNI:
Penampungan SITH-ITB, Account no : 0901062011
Identification and determination fee :
Rp. 55,000 (fifty five thousand rupiah) per plant sample,
Rp. 110,000 (one hundred and ten thousand rupiah) per animal sample
Specifically for Bachelor and Master student from SITH ITB, the identification fee is half of the normal fee. The student should write a request for the identification/determination. The letter should be signed by the student and co-signed by the student’s supervisor.
For private companies, the fee is twice the normal fee.
Payment can only done through the teller of the bank, with the following information provided:
- Name of the student making the payment.
- NPWP for the ones who already have one or personal identification number (No. KTP/ NIK)
- In the message collumn write the type of plants/animals to be identified/determined and the student’s name and registration number (NIM/ NPM)
- The photocopy of the request letter is handed together with:
- Proof of payment from Bank BNI
- Plant/animal specimen to be identified.
Requirements for the conditions of the plant specimen to be identified:
- Fresh plants or plants preserved in alcohol. Method of plant preservation to be used in determination: The plant should be wrapped in newspaaper and tied with a plastic raffia string. The wrapped plant is placed inside a transparent plastic bag and 70% alcohol is poured into the plastic bag. The plastic bag is then sealed with duct tape.
- For algae samples, the samples to be handed in have to be complete, that include the reproductive organs and the samples are placed inside an air tight container filled with 70% alcohol.
- For moss samples, the samples to be handed in are the whole parts of the moss, including the reproductive organs.
- For fern samples (pteridophytes), the samples to be handed in have to be complete, including the root, stem, sterile leaf without spores, fertile leaf with spores (Figure 1). Specifically for large ferns, bring a cut of the stem of the leaf and an intact sterile leaf and fertile leaf (Figure 2).
- For herbaceous plant samples, the samples to be handed in have to be complete, including the root, stem, leaf, flower and fruit (Figure 3). If the fruit is not available, than the flower would be sufficient. Specifically for large herbaceous plants such as red ginger (Etlingera elatior), tepus (Achasma megalacheilosor) or banana plant, bring the leaf, inflorescence and fruit (Figure 4).
- For bushes, shrubs and tree samples, the samples to be handed in are in the form of a 30 cm long branch, complete with leaves, flowers and fruits (Figure 5). The samples should be in an intact condition, consisting of branch, leaves, flowers and fruits. If the fruit is not available, the flower would be sufficient. .
- For bamboo samples, the samples to be handed in are a cut of the reed, midrib, leaf, and if possible the flower and fruit (Figure 6).
For rattan samples, the samples to be handed in are a cut of the stem, cut of the leaf stem, leaf, flagellum (usually located at the tip of the leaf), one inflorescence and fruit (Figure 7).

Figure 1. Sample of ferns. Parts that are handed in for determination are the roots, stem, sterile leaves and fertile leaves (Source of the picture: http://v3.boldsystems.org).

Figure 2. Samples of large ferns. Parts to be handed in are a cut og the leaf stem, complete sterile leaf and complete fertile leaf (Source of the picture: http://v3.boldsystems.org).

Figure 3. Samples of small herbaceous plants. Samples to be handed in for determination are the whole pant, complete with the root, stems, leaves, and reproductive organs (flowers and fruits) (Source of the picture: http://portal.cybertaxonomy.org).

Figure 4. Samples of large herbaceous plants. Samples to be handed in are the leaves, inflorescence and fruits (Source of the picture:: researchgate.net).

Figure 5. Samples of bushes, shrubs and trees. Samples to be handed in are a 30 cm long branch, complete with the leaves, flowers and fruits.


Figure 6. Samples of bamboo. Samples to be handed in are a cut of the reed, midrib, leaf, and if possible the reproductive organs (flowers and fruits) (Source of the picture: researchgate.net).

Figure 7. Samples of rattan. Samples to be handed in are a cut of the stem, cut of the leaf stem, leaf, flagellum and if possible, the reproductive organs (flowers and fruits) (Source of the picture: researchgate.net).
Requirements for the conditions of the animal samples to be identified:
Intact specimens with all body parts complete, no damaged or lost parts, handed in alive, have the following requirements:
- Specimens are adults (except for insect larvae) with a maximal size of 1 meter.
- Specimens are brought in a suitable substrate
- Sea water: for animals originating from the sea such as ocean fishes, sea cucumbers, crabs, shrimps, brine shrimps (Artemia), jelly fishes, squids, starfishes, sea slugs and sea urchins.
- Fresh water: for animals from fresh water such as freshwater fishes, eels, freshwater crabs, freshwater slugs, worms and water insects.
- Earth: for specimens that live underground such as earthworm and ground insects..
- Plant substrate in a container or cage for: specimens living in certain plants or specimens that could be kept in plant subtrates such as insects, amphibians, reptiles, chickens, birds and small mammals.
Specimens that are intact and well preserved, have the following requirements:
- Specimens have been fixed with 10% Neutral Buffered Formalin, with the following composition: 100 ml Formalin (37-40% stock solution), 900 ml Water, 4 grams sodium dihydrogen phosphate, monohydrate (NaH2PO4.H2O) and 6.5 grams disodium hydrogen phosphate, anhydrous (Na2HPO4). The recipe could be seen at http://stainsfile.info/StainsFile/prepare/fix/fixatives/formalin-buffered.htm
- The Neutral Buffered Formalin has to be injected into the specimen for animals with hard shells such as crabs, or have thick flesh and body cavity such as fishes, amphibians and reptiles. The specimens have to be incubated in the fixative solution for at least three days until the specimens are well fixed.
- After the specimens have hardened, they are rinsed with water to remove the Neutral Buffered Formalin untill the smell is not too strong.
- Specimens are placed in an air tight container (glass bottles, plastic containers or vials) that are filled with 70% alcohol (Figure 8).
- For large sized specimens (>50 cm), when the specimens are handed in, they should be wrapped in gauze that had been soaked in 70% alcohol and placed inside the container.

Figure 8. Example of a specimen that had been fixated with Neutral Buffered Formalin and soaked in 70% alcohol (Source of the picture: Royal BC Museum).
Intact specimens preserved in a freezer and handed in using an icebox.
Examples of specimens that could be handed in using this method are freshwater fishes, ocean fishes, shrimps, squids and jelly fishes (Figure 9).

Figure 9. Example of specimens preserved in an icebox (Source of the picture: http://www.coolersonsale.com).
- Plant/animal specimens are not advised to be entrusted to someone else.Directly bring the specimens with the proof of payment and the request for the identification or determination letter, the original as well as a copy, to:
Herbarium Bandungense and Zoology Museum Building, SITH – ITB
ITB Jatinangor Campus, Labtek V C, next to the Al-Jabbar Mosque.
Contact person for Plant Determination:
Arifin Surya Dwipa Irsyam B.Sc, M.Sc. (0857 8052 6704)
Contact person for Animal Determination:
email : museum-zoologi@sith.itb.ac.id
The letter of the results of the determination can be picked up at the Administration Office SITH ITB, Labtek XI Building, 1st floor, SITH ITB.
[:]

